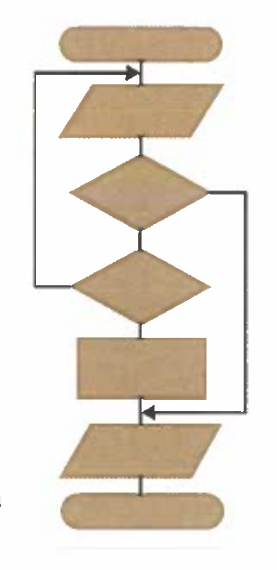
3 basic programming structures:
Structured programming approach aims to improve the clarity and maintainability of programs, and only the three control structures are allowed to use in block-strucutred languages

parallel computing: multiple processors each executing different instructions simultaneously
benefits
trade-offs
concurent processing: several processes are running, with each in turn being given a slice of processor time.
benefits
trade-offs
Divide and conquer reduces the size of the problem with every iteration binary search
Automation deals with building and putting into action models to solve problems.
Computers work with binary numbers but humans often prefer a visual image.
For example, we can represent the binary tree below in a diagram way.
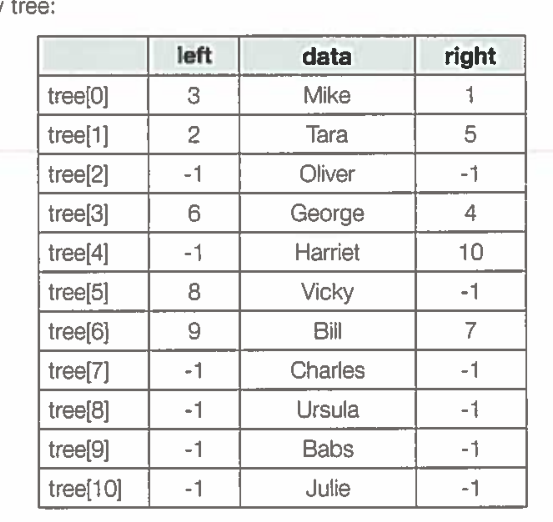 visualisation:
visualisation:
In some problems, in order to find a solution you have to make a series of decisions, but there may be cases for which:
Data mining is the process of digging through big data sets to discover hidden connections and predict future trends, typically involving the use of different kinds of software packages such as analytics tools. Big data is the term used for large sets of data that cannot be easily handled in a traditional database
although an algorithm may exist for their solution, it would take an unreasonably long time to find the solution.
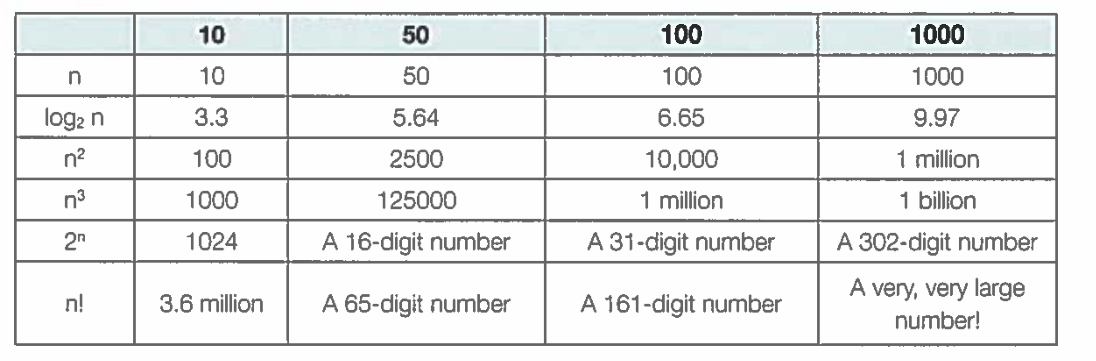
The table below shows what a huge difference there is in algorithms with different orders of time complexity for different values of n.
An approach to problem solving which employs an algorithm or methodology not guaranteed to be optimal or perfect, but is sufficient for the purpose
Performance modelling is the process of simulating different user and system loads on a computer using a mathematicl approximation, rather than doing actual performance testing which may be difficlt and expensive.
Pipelining is the technique of splitting tasks into smaller parts and overlapping the processing of each part of the task.